Benefits of Galvanizing
Lowest First Cost
Galvanizing is lower in first cost than many other commonly specified protective coatings for steel. (The application cost of labour intensive coatings such as painting has risen far more than the cost of factory operations such as galvanizing.)
Less maintenance / Lowest long term cost.
Even in cases where the initial cost of galvanizing is higher than alternative coatings, galvanizing is almost invariably cheapest in the long term (because it lasts longer and needs less maintenance). And, maintenance causes problems and adds to costs when structures are located in remote areas, and when plant shutdown or disruption to production is involved.
Long Life
The life expectancy of galvanized coatings on typical structural members is far in excess of 50 years in most rural environments, and 20 to 25 years plus, even in severe urban and coastal exposure.
Reliability
Galvanizing is carried out to Australian / New Zealand Standard 4680, and standard, minimum coating thicknesses are applied. Coating life and performance are reliable and predictable.
Toughest Coating
A galvanized coating has a unique metallurgical structure which gives outstanding resistance to mechanical damage in transport, erection and service.
Automatic protection for damaged areas
Galvanized coatings corrode preferentially to steel, providing cathodic or sacrificial protection to small areas of steel exposed through damage. Unlike organic coatings, small damaged areas need no touch up.
Complete protection
Every part of a galvanized article is protected, even recesses, sharp corners and inaccessible areas. No coating applied to a structure or fabrication after completion can provide the same protection
Ease of inspection
Galvanized coatings are assessed readily by eye, and simple non-destructive thickness testing methods can be used. The galvanizing process is such that if coatings appear sound and continuous, they are sound and continuous.
Faster erection time
As galvanized steel members are received they are ready for use. No time is lost on-site in surface preparation, painting and inspection. When assembly of the structure is complete, it is immediately ready for use, or for the next construction stage.
A full protective coating can be applied in minutes
The galvanizing process is not dependent on weather conditions
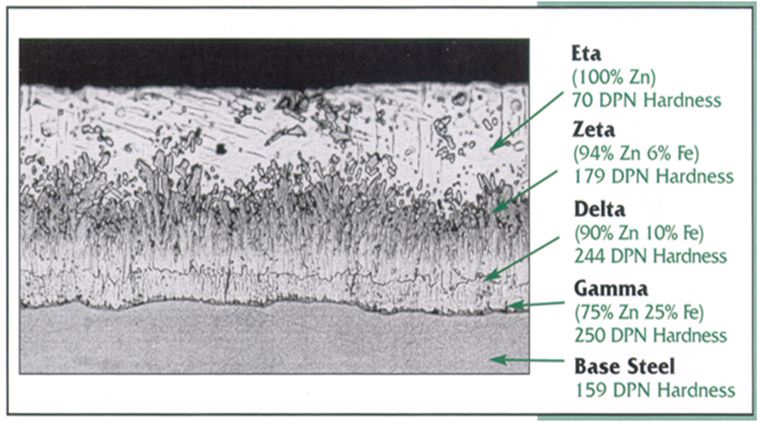
Galvanizing is a Metallurgical Bond
Unlike paint coatings Hot Dip Galvanizing fuses zinc with the iron in the steel to form permanent layers. This microscopic view displays the typical transition layers.
One Advantage of Galvanizing is Sacrificial Corrosion Protection or Self Healing Small area end cutting or local damage to a hot dip galvanized item is usually protected due to the surrounding zinc becoming an anode for the exposed steel.
Technical Supporting Information
As a long time member of the Galvanizers Association of Australia we can assist you with access to key information from an extensive source of print and electronic data, publications and case studies